
Interest rate decisions by central banks are pivotal in shaping economic landscapes and influencing borrowing costs, consumer behavior, and investment strategies. As we anticipate potential interest rate cuts in 2025, understanding their implications for the stock market becomes essential for investors, policymakers, and businesses alike.
Interest rate cuts occur when central banks, such as the Federal Reserve (Fed), reduce the benchmark interest rates to stimulate economic activity. Lower rates decrease borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, encouraging spending and investment. Historically, such monetary policy tools have been employed during economic slowdowns to spur growth. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed slashed rates to near zero to support the collapsing economy.
In this article, we're going to explain the mechanisms of interest rate cuts, examine historical precedents, and explore potential outcomes for the stock market.
As central banks worldwide have a big role in navigating inflation concerns, economic slowdowns, and shifting global trade dynamics, the likelihood of interest rate cuts in 2025 has gained significant attention. Various central banks, including the Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of England (BoE), and Bank of Japan (BoJ), have hinted at possible rate reductions to support economic stability.
Let's take a look at what to expect from major central banks in 2025 and how their decisions might shape global financial markets.
The U.S. Federal Reserve is at the center of global interest rate policy discussions. After aggressively raising rates to combat inflation in 2022 and 2023, the Fed paused rate hikes in late 2024, signaling a shift toward a more accommodative policy.
The Fed has cut rates 25 basis points in the January FOMC meeting, and it is expected to do another rate cut later this year. If inflation continues to decline toward the Fed’s target, policymakers may be more inclined to ease monetary policy. However, strong labor market data could delay the cuts. Investors have priced in 50 basis points of rate cuts, but Fed Chair Jerome Powell has emphasized a cautious approach, prioritizing economic stability over market pressures.
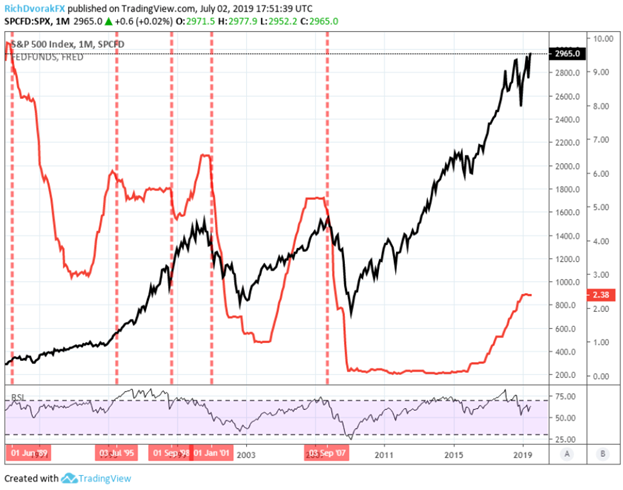
*S&P 500 Performance After Rate Cuts: The S&P 500 has historically gained about 4.9% one year after an initial rate cut, with positive returns 70% of the time. However, markets often dip in the first three months before rebounding by six months.
Key Considerations for the Fed's Rate Cuts:
In recent times, the Eurozone economy has faced sluggish growth and geopolitical challenges, including the Ukraine conflict and ongoing supply chain disruptions. The ECB raised interest rates aggressively in 2023 and 2024 to control inflation, but the economic slowdown has fueled expectations of policy easing in 2025.
The ECB has signaled rate cuts as early as mid-2025, but the exact timeline depends on inflation and economic growth data. Despite the inflation's cooling appeal in early 2025, it remained above the ECB’s 2% target. Unlike the Fed, the ECB might need to cut rates sooner to support economic recovery amid weak industrial output and low consumer spending. Some policymakers argue for a gradual approach, while others push for more aggressive cuts to prevent a prolonged recession.
Key Considerations for the ECB's Rate Cuts:
The Bank of England faces a complex challenge: balancing high inflation with slowing economic growth. In 2024, inflation in the UK remained stubbornly high, driven by housing costs, wage growth, and energy prices.
The BoE is expected to cut rates in the second half of 2025, following inflation improvements. However, considering the trade war situation with the U.S. President Trump's tariffs, there may be different decisions. In addition, high wage growth has kept inflation elevated, making it harder for the BoE to justify rate cuts too early. Markets expect at least two rate cuts, but the BoE remains more cautious than the Fed or ECB.
Key Considerations for the BoE's Rate Cuts:
Unlike other major central banks, the Bank of Japan (BoJ) has maintained ultra-low interest rates for decades. Japan has struggled with deflation and low economic growth, but recent inflationary pressures have prompted speculation about policy normalization.
The BoJ might raise rates slightly instead of cutting them, making it the outlier among central banks. Higher inflation in Japan could push the BoJ to end its negative interest rate policy, moving toward a more balanced stance. Global rate cuts might limit the BoJ’s ability to increase rates significantly without impacting currency stability.
Key Considerations for the BoJ's Rate Decisions:
The stock market is expected to experience significant shifts in valuation, investor sentiment, and sector performance due to the preparations for the potential interest rate cuts. The exact impact will depend on various factors, including economic growth, corporate earnings, and market expectations.
Let’s explore how rate cuts influence stock markets, which sectors may benefit or struggle, and key investor considerations for 2025.
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Stock Markets
Interest rates and stock prices have an inverse relationship. When central banks lower rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging business investment, consumer spending, and corporate growth. This tends to increase stock valuations as investors anticipate stronger earnings and economic expansion.
Key Ways Interest Rate Cuts Affect Stocks:
However, not all rate cuts are positive for stocks. If markets perceive rate reductions as a response to economic distress, investor confidence may erode, triggering volatility or selloffs in riskier assets.
Historical data suggests that rate cuts generally provide a bullish environment for equities, though outcomes vary based on economic conditions and investor sentiment.
Key Historical Trends:
While rate cuts often boost stocks, market reactions depend on whether investors see them as proactive support or a response to economic weakness.
Not all sectors react the same way to interest rate cuts. While most industries see improved financial conditions, certain sectors historically outperform in a low-rate environment.
Sectors Expected to Benefit from Rate Cuts in 2025:
Here are the sectors that are expected to benefit from the rate cuts:
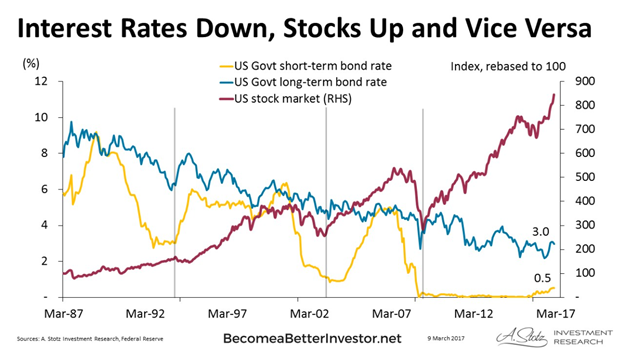
*Market Highs and Rate Cuts: When the Fed cuts rates near market highs, the S&P 500 has consistently posted gains 12 months later, highlighting a strong market response.
Lower rates reduce borrowing costs for innovation and expansion. Tech firms rely on long-term projections and benefit from discounted future cash flows. For example, the Nasdaq Composite surged after previous rate cuts as investors favored high-growth tech companies.
Lower mortgage rates improve home sales and commercial property demand. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) borrow heavily, so cheaper debt financing improves profitability. The housing market tends to heat up after rate cuts, driving demand for residential and commercial properties.
With lower borrowing costs, consumer confidence rises, leading to higher spending on luxury goods, travel, and entertainment. Companies selling autos, high-end fashion, and leisure services tend to see increased demand. Past rate cuts have fueled higher spending in companies like Tesla, Nike, and Disney.
While rate cuts lower profit margins for banks, increased loan demand can offset losses. Asset managers benefit as stock market gains boost assets under management (AUM). Usually, investment firms and wealth managers thrive in bull markets fueled by lower rates.
Companies in infrastructure, transportation, and heavy equipment see higher capital investment. Rate cuts increase business spending, leading to higher demand for machinery and logistics. Aerospace, automotive, and engineering firms often outperform in low-rate environments.
While rate cuts create many winners, some sectors face challenges due to economic adjustments or shifting investor priorities.
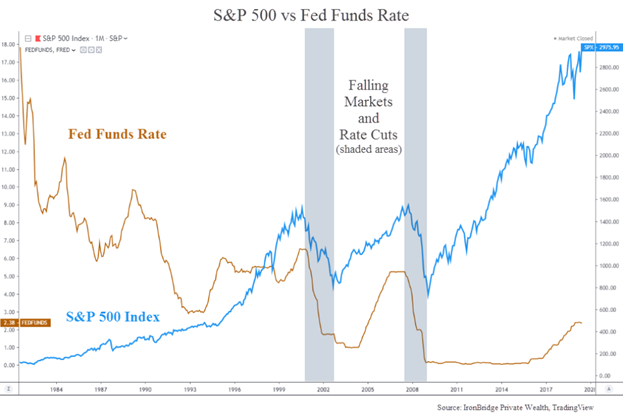
*Sectoral Performance During Rate Cuts: Bonds tend to perform well during rate cuts, while stocks and real estate often decline, with stocks seeing the biggest losses.
Sectors That May Face Challenges in 2025:
Here are the sectors that are expected to face challenges from the rate cuts:
Investors often shift away from defensive sectors like utilities and staple goods when growth stocks outperform. Dividend-paying stocks become less attractive if bond yields decline. Utility stocks may underperform relative to tech and consumer discretionary stocks.
Lower rates can weaken the U.S. dollar, making commodities like oil and natural gas more expensive. If rate cuts signal an economic slowdown, demand for energy may soften. Oil prices could experience volatility if global demand expectations shift.
Lower interest rates reduce banks' profit margins on loans. While rate cuts increase loan demand, they also reduce banks’ net interest income. Large commercial banks may struggle, while investment-focused financial firms may benefit.
With rate cuts on the horizon, investors could consider the following strategies:
While interest rate reduction normally creates positive trends for equities, their influence in 2025 will depend on a number of factors, including:
How do interest rate cuts influence corporate earnings?
Lower interest rates reduce borrowing costs for companies, allowing them to finance operations and expansions more cheaply. This can lead to increased profitability, which often support stock valuations.
Are there risks associated with investing in stocks during periods of falling interest rates?
Yes, while lower interest rates can stimulate economic activity, they may also lead to excessive speculation, inflated asset prices, and potential market bubbles. Investors should remain cautious and consider the broader economic context.
How might anticipated interest rate cuts in 2025 affect dividend-yielding stocks?
Dividend-yielding stocks, such as those in the utilities and consumer staples sectors, may become less attractive if bond yields decline, leading investors to seek higher returns elsewhere.
Could interest rate cuts in 2025 lead to currency fluctuations that impact multinational companies?
Yes, rate cuts can weaken a country's currency, benefiting multinational companies with overseas revenue, as their foreign earnings translate into higher domestic profits.
How can investors adjust their portfolios in anticipation of interest rate cuts?
Investors might consider increasing allocations to sectors that benefit from lower borrowing costs, such as technology and consumer discretionary industries while maintaining diversification to mitigate potential risks.
Would like to learn how to look financial markets from a different angle? Then keep reading and invest yourself with ZitaPlus.